字符串
遍历器接口
1 | for (let str of 'foo') { |
includes()
- 功能:返回布尔值,表示是否找到了参数字符串
startsWith()
- 功能:返回布尔值,表示是否在原字符串的头部
endsWith()
- 功能:返回布尔值,表示是否在原字符串的尾部
这三个方法只传一个参数时
1
2
3
4let s = 'zhangpanpan'
console.log(s.includes('z'))//true
console.log(s.startsWith('zha'))//true
console.log(s.endsWith('pan'))//true传入第二个参数时,表示开始搜索的位置
1
2
3
4let s = 'zhangpanpan'
console.log(s.includes('z', 0))//true
console.log(s.startsWith('zha', 1))//false
console.log(s.endsWith('pan', 8))//true
repeat()
- 功能:返回一个新字符串,表示原字符串重复n次
- 案例
1
2console.log('x'.repeat(3))//xxx
console.log('x'.repeat(0))//""
padStart(),padEnd()
- 功能:字符串补全功能
- 案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10// 参数1:字符串的最小长度
// 参数2:用来补全的字符串
// 从头部开始补全
console.log('x'.padStart(5, 'abc'));//abcax
// 从尾部开始补全
console.log('x'.padEnd(6, 'abc'));//xabcab
// 如果字符串的指定长度小于原来的长度,则返回原字符串
// 如果省略了第二个参数,则使用空格补全
console.log('2'.padStarts(2, '0')); //02
模板字符串
1 | let name = 'zpp'; |
正则
正则方法
reg.exec(str):检索字符串中指定的值,返回找到的值,并确定其位置
1
2
3var reg = /\d/g;
var str = 'c2cw3';
console.log(reg.exec(str))//2reg.test(str):检索字符串中指定的值。返回true或者false
1
2
3
4
5
6var reg = /\d/g
var str = 'c2cw3'
var str2 = 'qqq'
console.log(reg.test(str))//true
console.log(reg.test(str2))//false
String对象的方法
str.serach(reg)方法不执行全局匹配,它将忽略标志g。它的返回值是检索的位置,若没有返回-1
1
2
3
4
5var reg = /\d/g;
var str = '12cd3'
var str2 = 'aa'
console.log(str.search(reg))//0
console.log(str2.search(reg))//-1str.match(reg)方法找到一个或者多个正则表达式的匹配,返回是指定的值,是一个数组,若没有匹配的结果则返回null
1
2
3
4
5
6
7var reg = /\d/g;
var reg2 = /\d+/g;//匹配多个数字,要有g
var str = '12cd3'
var str2 = 'aaa'
console.log(str.match(reg)) // ["1", "2", "3"]
console.log(str.match(reg2)) // ["12", "3"]
console.log(str2.match(reg))// nullstr.replace(reg|str, str)替换与正则表达式匹配的子串
一些字符替换另一些字符,或替换一个与正则表达式匹配的子串
1
2
3var reg = /\d/g;
var str = '12cd3';
console.log(str.replace(reg, 'xx')) // xxxxcdxx如果第一个参数传入的是带分组的正则表达式。我们在第二个参数中可以使用一下来获取相应的分组
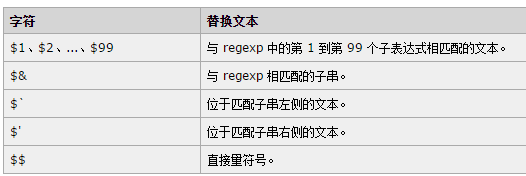
1
2
3var str2 = '<%11%><%4a%><%3%>'
var ret = str2.replace(/<%([^%>]+)%>/g, '@#$1#@');
console.log(ret)//@#11#@@#4a#@@#3#@str.replace(reg, function(){})把replace方法的第二个参数传入一个function,,这个function会在每次匹配替换的时候调用,算是个每次替换的回调函数,我们使用了回调函数的第一个参数,也就是匹配内容,其实回调函数一共有四个参数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10// 第一个参数很简单,是匹配字符串
// 第二个参数是正则表达式分组内容,没有分组则没有该参数
// 第三个参数是匹配项在字符串中的index
// 第四个参数则是原字符串
var ret2 = str2.replace(/<%([^%>]+)%>/g, function(a, b, c, d){
console.log(a)
console.log(b)
console.log(c)
console.log(d)
})str.split(reg/需要分割的标识, 取返回数组的长度)用于把一个字符串分割成字符串数组,返回数组
1
2
3var reg = /\d/g;
var str = '12cd3';
console.log(str.split(reg, 4))// ["", "", "cd", ""]
数值
函数
数组
扩展运算符(…)
- 功能:将一个数组转为用逗号分隔的参数序列。主要用于函数调用。
- 案例
1
2
3
4
5function add(x, y) {
return x + y;
}
let item = [1, 20]
console.log(add(...item))// 21
Array.from(object)
- 功能:用于将两类对象转为真正的数组:类似数组的对象(array-like object)和可遍历(iterable)的对象(包括 ES6 新增的数据结构 Set 和 Map)
- 案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9let arrayLike = {
'0': 'a',
'1': 'b',
'2': 'c',
length: 3
}
// es5
// console.log([].slice.call(arrayLike)) // ['a', 'b', 'c']
console.log(Array.from(arrayLike))
Array.of()
- 功能:将一组值转化为数组
- 案例
1
console.log(Array.of(1, 2,3))// [1, 2, 3]
数组实例copyWithin
- 功能:将指定位置的成员复制到指定位置(会改变原数组)
- 案例
1
2
3
4
5let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
// target: 开始替换位置的索引值
// start: 从该位置读取数据,默认是0
// end: 到此位置读取数据结束,默认是数组长度
console.log(arr.copyWithin(0, 3, 5)); //[4, 5, 3, 4, 5]
数组实例find()和findIndex()
- 功能1:find()找到第一个符合条件的数组成员,参数是callback, return: 该成员 || undefined
- 功能2: findIndex()找到第一个符合添加的数组成员的位置,没有就返回-1
- 案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17let findFirst = [1, 2, 0, -3].find((n, index, arr)=> {
//n:当前值
// index: 当前的索引
// arr:原数组
return n < 0;
});
let findFirstIndex = [1, 2, NaN, -3].findIndex((n, index, arr)=> {
//n:当前值
// index: 当前的索引
// arr:原数组
return n < 0;
});
// 弥补了indexOf的不足,可以发现NaN
let findNaN = [1, NaN].findIndex(n => Object.is(NaN, n))
console.log(findFirst)// -3
console.log(findFirstIndex)// 3
console.log(findNaN)//1
数组实例fill()
- 功能:使用给定值,填充一个数组
- 案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7let sourceArr = [1, 3, 5];
let targetArr = sourceArr.fill('a');
console.log(targetArr) // ['a', 'a', 'a']
// 参数1:指定的填充数据
// 参数2:用于填充的起始位置
// 参数3:用于填充的结束位置(不包括结束位置)
console.log([1, 2, 4, 5].fill('a', 1, 2)) // [1,'a', 4,5]
数组实例entries(),keys()和values()
- 功能: 都是用于遍历数组,都返回一个遍历器对象。唯一的区别是keys()是对键名的遍历、values()是对键值的遍历,entries()是对键值对的遍历
- 案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17for (let index of ['a', 'b'].keys()) {
console.log(index);
}
// 0
// 1
for (let elem of ['a', 'b'].values()) {
console.log(elem);
}
// 'a'
// 'b'
for (let [index, elem] of ['a', 'b'].entries()) {
console.log(index, elem);
}
// 0 "a"
// 1 "b"
数组实例includes()
- 功能: 表示某个数组是否包含给定的值,返回Boolean
- 案例
1
2
3
4console.log([1, 2, 3].includes(2))// true
console.log([1, 2, 3].includes('e'))// false
// 参数2:表示搜素的起始位置,默认为0
console.log([1, 2, 3].includes(2, 3))// false
对象
对象的简便写法
- es6允许直接写入变量和函数,作为对象的属性和方法
- 案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17// 变量
const foo = 'bar'
const baz = {foo}
console.log(baz.foo)// bar
// 函数
function foo(x, y) {
return {x, y}
}
console.log(foo(1, 2)) // {x: 1, y: 2}
// 方法简写
const o = {
method() {
return "Hello!";
}
}
方法的name属性
- 案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7const person = {
sayName() {
console.log('Hello')
}
}
// name属性是返回函数的属性名
console.log(person.sayName.name)// sayName
- 案例
Object.is()
- 功能:它用来比较两个值是否严格相等
- 案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7console.log(Object.is('foo', 'foo')) // true
console.log(Object.is({}, {})) // false
console.log(+0 === -0) // true
console.log(NaN === NaN) // false
console.log(Object.is(-0, +0)) // false
console.log(Object.is(NaN, NaN)) // true
Object.assign()
- 功能:用于对象的合并,将源对象(source)的所有可枚举属性,复制到目标对象(target)。
案例
1
2
3
4
5const target = {a:1};
const target2 = {b:2}
// 参数1:目标对象,其他参数:原对象
let obj = Object.assign({}, target, target2);
console.log(obj) // {a: 1, b: 2}tips: 如果目标对象与源对象有同名属性,或多个源对象有同名属性,则后面的属性会覆盖前面的属性。
- 注意点:浅拷贝,同名属性替换,
属性的可枚举性和遍历
可枚举性
- Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor方法可以获取该属性的描述对象
- 案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8let obj = {foo: 123}
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, 'foo'))
// {
// configuration: true,
// enumerable: true,
// value: 123,
// writable: true
// }
属性的遍历
- for…in循环遍历对象自身的和继承的可枚举属性
- Object.keys(obj)返回一个数组,包括对象自身的(不含继承的)所有可枚举属性(不含 Symbol 属性)的键名。
- Object.getOwnPropertyNames(obj)返回一个数组,包含对象自身的所有属性(不含 Symbol 属性,但是包括不可枚举属性)的键名。
- Object.getOwnPropertySymbols(obj)返回一个数组,包含对象自身的所有 Symbol 属性的键名。
- Reflect.ownKeys(obj)返回一个数组,包含对象自身的所有键名,不管键名是 Symbol 或字符串,也不管是否可枚举。
